What Is Error 404?
This error code occurs when the web server fails to find a resource, like a website at a given URL. You’ll usually encounter this problem when:
- The website has been deleted and is no longer available on the server
- You entered the wrong website URL
- The website changed the URL linking to a page or resource
- The owner misconfigured the website
404 errors on websites can be scary, especially for website owners since it means that people can’t see or visit their website.
However, they aren’t usually a bad thing.
As it turns out, they can also help search engines index and rank your pages.
In this guide, we’ll tell you everything about the error 404, including its impact on your website. You’ll also learn how to spot error 404 on your website and how you can fix them.
What Do Visitors See In Error 404?
The error 404 has no specific appearance.
What visitors see varies depending on the website’s configuration, some display it as simple as text, while others include images and detailed information about the error.
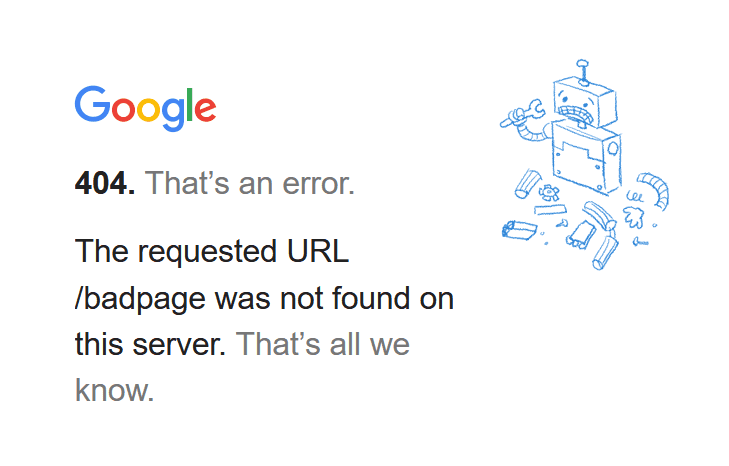
404 error pages can also include messages like:
- The page you’re trying to access doesn’t exist
- The requested URL can’t be found
- The page has been moved or deleted
If there’s one thing that 404 errors have in common, it would be the code that gave them their name.
HTTP Status Codes
HTTP status codes are three-digit responses that are relayed every time you visit a website.
Whenever you visit a URL or click a link, your browser sends a request to that website’s server and it responds with an HTTP code that tells your browser more about that page.
The HTTP code sent by site servers has a whole system and each number has a corresponding meaning:
- 1XX (Information Code) – sent when the server acknowledges and processes the request.
- 2XX (Success Code) – sent when the server successfully received and processed the request.
- 3XX (Redirection Code) – sent when the server receives the request but there’s a redirect to another page or website.
- 4XX (Client Error Code) – sent when the server could not find or reach the website.
- 5XX (Server Error Code) – sent when the client made a valid request but the server can’t complete it.
With the information above, we can see that the “404” code falls under “Client Error Code”, which indicates that the URL or website can’t be found.
Checking Website HTTP Status Code
If you want to check a website or page status code, you can do it by:
- Open any web browser and visit httpstatus.io.
- Enter the site URL in the textbox.
- Click Check Status.
You’ll see the URL’s status code below the “Check Status” button.
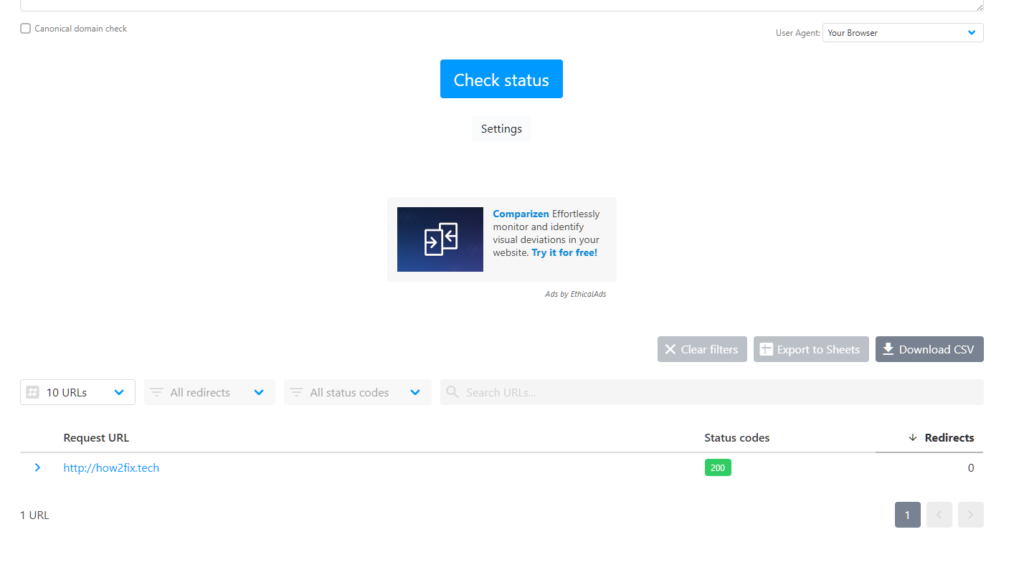
Hard vs Soft Error 404
- Hard 404 Error – refers to a situation where the requested resource is permanently gone. This means that the server has a clear indication that the website no longer exists and will not exist in the future. This is usually the case when a website is deleted or moved without a proper redirection set up.
- Soft 404 Error – occurs when a page that doesn’t exist returns a 200 OK status code instead of a proper 404 status. This means that the server might serve a page with content, but that content indicates that the page doesn’t exist. This also confuses search engines and users as it suggests that the page exists when it doesn’t/
Example:
Let’s take a look at this sample. If we visit https://how2fix.tech/abcd, it will show a 404 error with the website’s interface and other elements being present.
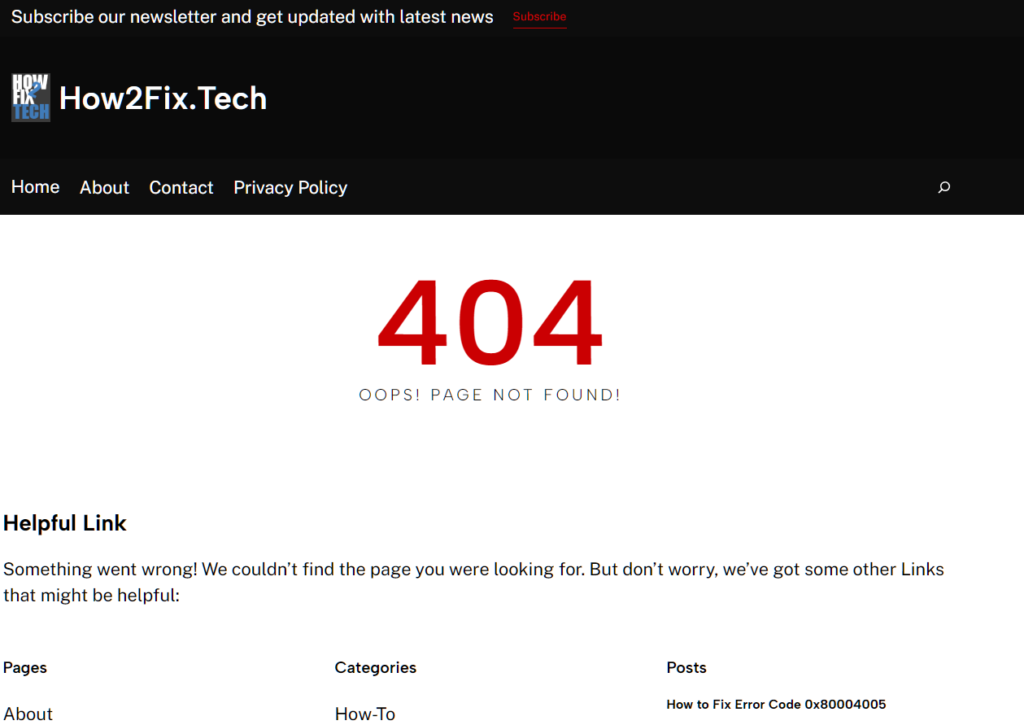
This is what we call a soft 404 error. The website returns a 200 OK status, but the actual page that is shown indicates that the page we are trying to visit doesn’t exist.
Effects of 404 Errors On Websites
- Poor User Experience: When users encounter 404 errors, it disrupts their browsing experience. It prevents them from accessing the content they were seeking, leading to frustration and potentially driving them away from the site. This negative experience can impact their perception of the website and the brand it represents.
- Decreased Engagement: Users who encounter 404 errors are less likely to engage further with the website. They may abandon their current session or even leave the site altogether, resulting in decreased page views, time on site, and interactions with other content.
- Lost Opportunities: 404 errors represent missed opportunities for engagement, conversion, or other desired actions. If the missing page contains important information, products, or services, the website loses the chance to fulfill user needs, address inquiries, or convert visitors into customers.
- Negative Impact on SEO: Search engines may interpret 404 errors as a sign of poor website maintenance or outdated content. Continuously encountering such errors can harm the website’s search engine ranking and overall visibility. Additionally, if the missing pages had valuable backlinks, the loss of those links can further impact SEO performance.
- Broken Links and Reputation Damage: Outdated or broken links leading to 404 errors can damage the website’s reputation and credibility. Visitors may perceive the site as unreliable or poorly maintained, affecting their trust in the brand and potentially deterring future visits or interactions.
- Impaired Indexing and Crawling: Search engine bots encountering numerous 404 errors may spend less time crawling and indexing the website, focusing instead on pages that provide value and relevance. This can lead to slower updates in search engine results and reduced visibility for new or updated content.
Identifying 404 Errors On Website
1. Manual Checking
The most straightforward way to spot 404 errors on your website is to manually browse your site and click on links to see if they lead to valid pages. Keep an eye out for any “Page Not Found” messages or broken links.
2. Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a powerful tool that can provide you with helpful metrics and information about your website’s health and performance. This includes crawl errors such as 404s.
3. Third-Party Tools
Many website analytics tools, such as Google Analytics, provide reports on 404 errors encountered by users. Look for sections or reports related to site errors or broken links.
There are also numerous third-party tools available that can scan your website for broken links and report any 404 errors they find. Some popular options include Screaming Frog SEO Spider, Moz Link Explorer, and Broken Link Checker.
4. Server Logs
Server logs contain records of all requests made to your website, including requests for pages that result in 404 errors. Analyzing server logs can help you identify patterns of 404 errors and pinpoint their sources.
5. Website Monitoring Services
Consider using website monitoring services that regularly check your website for errors, including 404s, and alert you when they occur. These services can provide real-time notifications and help you quickly address any issues.
Fixing Error 404s On Website
Fixing 404 errors on websites involves several steps to ensure that visitors can access the content they are looking for.
Here’s a guide on how to address and resolve 404 errors:
- Identify Broken Links: Use website auditing tools, server logs, or Google Search Console to identify the URLs that are generating 404 errors. Determine the source of the broken links, whether they are internal links within your website or external links from other sites.
- Redirect or Update Links: Once you’ve identified the broken links, take action to redirect them to relevant, existing pages on your website. You can set up 301 redirects, which permanently redirect users and search engines to a new URL. Alternatively, update the links to point to the correct URLs if the content has been moved or renamed.
- Customize 404 Error Page: Create a custom 404 error page to provide users with helpful information when they encounter a broken link. Include a brief explanation of what went wrong, a search bar or navigation links to help users find what they are looking for, and a contact form or link to report the error.
- Monitor and Test Regularly: Continuously monitor your website for broken links and 404 errors using tools like Google Search Console or website auditing tools. Regularly test internal and external links to ensure they are functioning correctly and update them as needed.
- Check Server Configuration: Sometimes, 404 errors can be caused by server misconfigurations or issues with URL rewriting rules. Review your server configuration files, such as .htaccess (for Apache servers) or web.config (for IIS servers), to ensure they are correctly configured to handle URL redirects and rewrite rules.
- Provide Feedback to Users: When users encounter a 404 error, provide clear feedback and guidance on how to proceed. Avoid generic error messages and instead offer helpful suggestions, such as alternative links or a search function to help users find the content they were looking for.
By following these steps, you can effectively fix 404 errors on your website and improve the overall user experience by ensuring that visitors can access the content they are seeking.
When to Fix A 404 Error On Website
Determining whether your website’s 404 errors need fixing depends on your intentions for the pages in question.
- Unwanted Pages: If you’re intentionally removing pages from your website and don’t want users to access them, then it’s appropriate for those pages’ URLs to return 404 errors. This signals to search engines that the content is no longer available for indexing or ranking.
- Desired Pages: However, if you still want to showcase and drive traffic to the pages generating 404 errors, then addressing these errors becomes necessary. In this case, fixing the 404 errors ensures that users can access the intended content, improving their browsing experience and potentially enhancing your website’s performance in search engine results.
Ultimately, the decision to fix 404 errors depends on your strategic goals for the affected pages and how you want them to be perceived by both users and search engines.




Leave a Reply